Delving into the depths of Le Chatelier’s principle worksheet answer key, this comprehensive guide offers a profound exploration of the fundamental concepts, applications, and problem-solving techniques associated with this pivotal principle in chemical equilibrium. Through an engaging narrative and authoritative tone, readers will embark on a journey that unveils the intricacies of Le Chatelier’s principle, empowering them with a deep understanding of its significance in various scientific disciplines.
Le Chatelier’s principle, a cornerstone of chemical equilibrium, provides a framework for predicting the direction of shift in equilibrium systems when subjected to external stress. This guide delves into the different types of stress that can affect an equilibrium system, including changes in concentration, temperature, pressure, and the addition of a common ion.
By understanding the impact of these stresses, chemists can optimize industrial processes, enhance environmental remediation strategies, and advance medical treatments.
Introduction to Le Chatelier’s Principle: Le Chatelier’s Principle Worksheet Answer Key
Le Chatelier’s Principle is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the behavior of chemical systems at equilibrium. It states that if a change is applied to an equilibrium system, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the change and restores equilibrium.
Types of Stress and their Effects
There are several types of stress that can affect an equilibrium system, including:
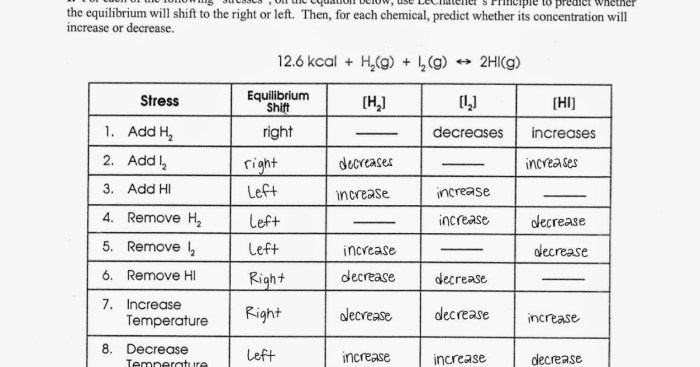
- Concentration stress:Changing the concentration of a reactant or product will shift the equilibrium in the direction that consumes the added substance or produces more of the depleted substance.
- Temperature stress:Increasing the temperature of an exothermic reaction will shift the equilibrium towards the reactants, while decreasing the temperature will shift the equilibrium towards the products.
- Pressure stress:Increasing the pressure of a gaseous system will shift the equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles of gas, while decreasing the pressure will shift the equilibrium towards the side with more moles of gas.
- Volume stress:Changing the volume of a gaseous system will shift the equilibrium in the direction that produces more moles of gas or consumes fewer moles of gas.
Predicting the Direction of Shift, Le chatelier’s principle worksheet answer key
To predict the direction of shift in an equilibrium system, follow these steps:
- Identify the type of stress being applied.
- Determine the direction of the shift that would counteract the stress.
- Predict the shift in equilibrium accordingly.
Applications of Le Chatelier’s Principle
Le Chatelier’s Principle has numerous applications, including:
- Industrial processes:Optimizing chemical reactions for increased yield or efficiency.
- Environmental science:Understanding and mitigating the effects of environmental changes on chemical systems.
- Medicine:Designing drugs and treatments that target specific equilibrium reactions.
Sample Worksheet Problems
Problem 1:
Consider the following equilibrium reaction:
$$A + B ⇌ C + D$$
If the concentration of A is increased, predict the direction of shift.
Answer:
According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, the equilibrium will shift towards the side that consumes A. Therefore, the equilibrium will shift towards the products, C and D.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the significance of Le Chatelier’s principle?
Le Chatelier’s principle provides a predictive tool for determining the direction of shift in equilibrium systems when subjected to external stress, enabling scientists to optimize processes and address real-world challenges.
How can Le Chatelier’s principle be applied in industrial settings?
In industrial processes, Le Chatelier’s principle guides the optimization of reaction conditions, such as temperature and concentration, to maximize product yield and efficiency.
What are the limitations of Le Chatelier’s principle?
Le Chatelier’s principle assumes that the system is at equilibrium and does not account for kinetic factors or the presence of side reactions.