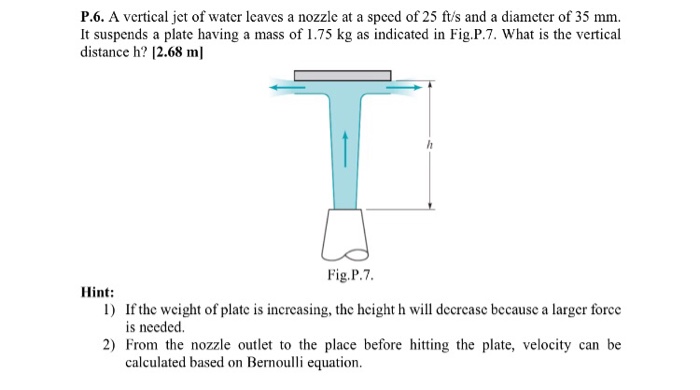
A vertical jet of water leaves a nozzle – A vertical jet of water leaving a nozzle is a fascinating phenomenon with a wide range of applications in industry and everyday life. Understanding the physics behind this phenomenon is crucial for designing and utilizing water jets effectively.
This article delves into the intricate details of vertical water jets, exploring their behavior, applications, design considerations, and safety measures. It also examines the latest advancements and potential future applications of this versatile technology.
Description of the Phenomenon
A vertical jet of water is a column of water that is ejected upwards from a nozzle. The physics behind this phenomenon can be explained by the principle of conservation of energy. As the water flows through the nozzle, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
This kinetic energy is then used to propel the water upwards against the force of gravity.
The height and shape of the jet are affected by a number of factors, including the diameter of the nozzle, the velocity of the water, and the density of the water. The diameter of the nozzle determines the amount of water that can flow through the nozzle, which in turn affects the velocity of the water.
The velocity of the water determines the height of the jet, while the density of the water affects the shape of the jet.
Applications of Vertical Water Jets
Vertical water jets are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Firefighting:Vertical water jets can be used to extinguish fires by cooling the fuel and preventing the spread of flames.
- Industrial cleaning:Vertical water jets can be used to clean surfaces, such as tanks, pipes, and machinery.
- Mining:Vertical water jets can be used to break up rocks and minerals.
- Entertainment:Vertical water jets are often used in fountains and other water features.
Vertical water jets offer a number of advantages over other methods of delivering water. They are relatively inexpensive to operate, they can be used in a variety of applications, and they are environmentally friendly.
Design Considerations for Vertical Water Jets
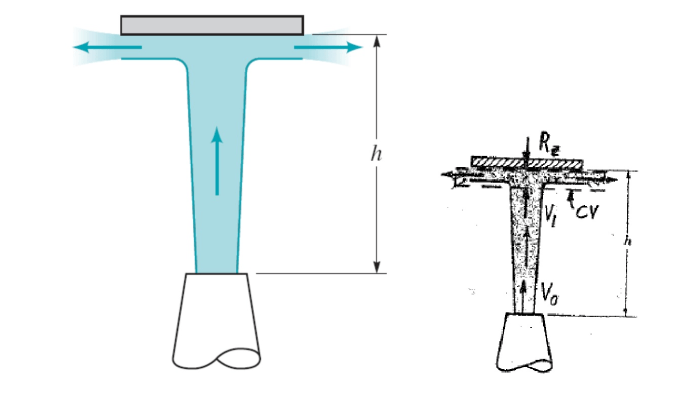
When designing a vertical water jet system, there are a number of key parameters that need to be considered. These parameters include:
- Nozzle diameter:The diameter of the nozzle determines the amount of water that can flow through the nozzle, which in turn affects the velocity of the water.
- Water velocity:The velocity of the water determines the height of the jet.
- Water density:The density of the water affects the shape of the jet.
- Nozzle angle:The angle of the nozzle determines the direction of the jet.
- Pipe diameter:The diameter of the pipe that supplies water to the nozzle affects the velocity of the water.
The design of a vertical water jet system is a complex process that requires careful consideration of all of the relevant parameters.
Safety Considerations for Vertical Water Jets: A Vertical Jet Of Water Leaves A Nozzle
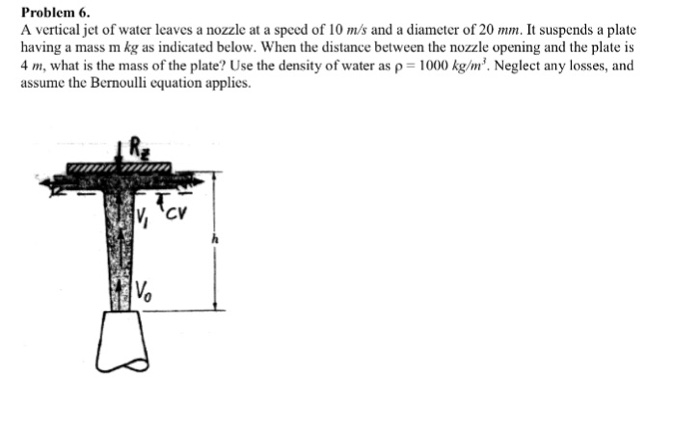
Vertical water jets can be hazardous if they are not used properly. The following safety precautions should be taken when using vertical water jets:
- Never point a vertical water jet at people or animals.
- Always wear eye protection when using a vertical water jet.
- Be aware of the surroundings and make sure that there are no obstacles in the path of the jet.
- Never use a vertical water jet in a confined space.
By following these safety precautions, you can help to prevent accidents when using vertical water jets.
General Inquiries
What factors affect the height and shape of a vertical water jet?
The height and shape of a vertical water jet are influenced by factors such as nozzle diameter, water pressure, fluid velocity, and environmental conditions.
What are some common applications of vertical water jets?
Vertical water jets are used in various applications, including fire suppression, industrial cleaning, cutting and shaping materials, and aeration.
What safety considerations should be taken when using vertical water jets?
Potential hazards associated with vertical water jets include high-pressure water, electrical hazards, and slippery surfaces. Proper safety measures, such as wearing protective gear and ensuring proper grounding, should be implemented.